Teams from Red Hat and NVIDIA have collaborated on creating a scalable hybrid cloud application that could revolutionize smart city initiatives such as traffic-flow monitoring and transportation management around the world. By working together, the two companies are creating solutions that make cities smarter and more efficient by taking sensor data and processing it in real-time to provide insights for traffic congestion, pedestrian flow, and infrastructure maintenance.
Running on top of the NVIDIA EGX platform with the NVIDIA GPU Operator, the application is built with NVIDIA’s Metropolis application framework for IoT that brings together innovative capabilities for real-time image processing where NVIDIA DeepStream SDK is used to extract metadata from live video streams at the edge. It then forwards the right metadata to the cloud for deeper analytical processing and further representation in an information dashboard depicted below.
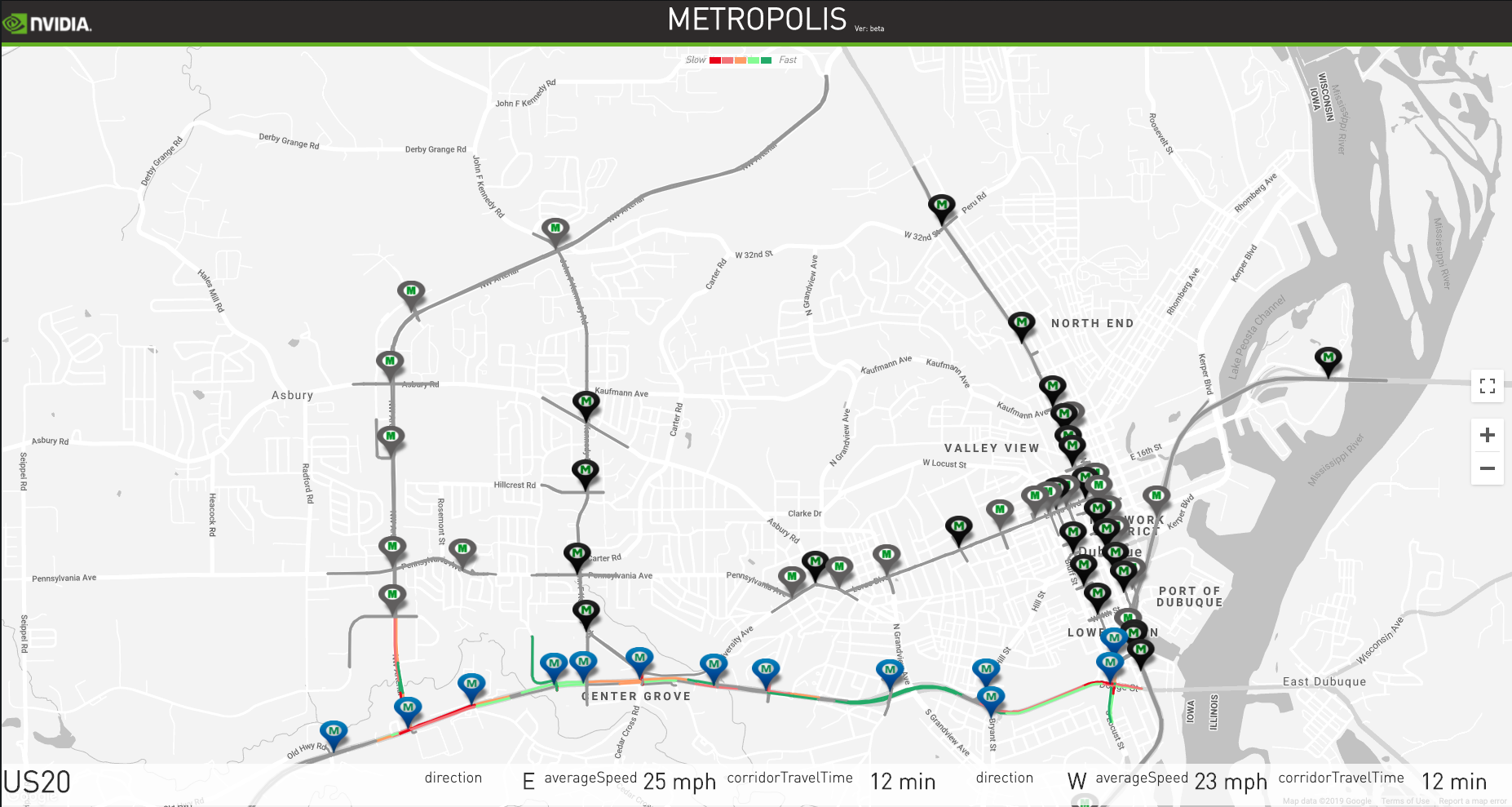
The browser-based user interface (UI), showing camera placement at traffic intersections
As part of this collaboration, the analytics service platform for NVIDIA Metropolis is provided by Red Hat OpenShift, the industry’s most comprehensive enterprise Kubernetes platform for modern hybrid cloud application development and deployment. Applications are deployed as container-based microservices into an OpenShift cluster running in the cloud and the cluster is responsible for orchestrating the container deployments, maintaining their replicas, and monitoring system health to provide high availability and scalability. The figure below gives an overview of the data flow and solution architecture.

NVIDIA Metropolis in the hybrid cloud: NVIDIA EGX on the left, OpenShift in the public cloud on the right
The NVIDIA Metropolis software functionality is provided by a combination of NVIDIA-developed reference applications and open source components deployed into an OpenShift cluster from an embedded service catalog called the OperatorHub. Operators are extensions for Kubernetes that make use of custom resources to minimize the burden of manually installing and configuring the various resources for complex software clustered-services, such as Elasticsearch, Apache Kafka, and Apache Spark. OpenShift includes its own enterprise OperatorHub with over 40 OpenShift Certified Operators that have been tested and supported by Red Hat and its partner ecosystem. In addition to those, the public OperatorHub.io today provides more than 80 community Operators. Community Operators broaden the choices for other Kubernetes distributions across different categories, ranging from databases to artificial intelligence (AI) / machine learning (ML) applications.

Two Operators used by the NVIDIA Metropolis application: Apache Spark and Strimzi Kafka
The OpenShift cluster is hosted in the cloud comprised of three master nodes for the control plane and 10 worker nodes, each with 16 vCPU and 64GB of memory. The application and the cluster can be elastically scaled based on real-time demand. Machine resources (worker nodes) can easily be added or removed using the OpenShift console. The number of running replicas for any of the components within the NVIDIA Metropolis application could be easily adjusted with an edit of a field in the console. In both cases, OpenShift immediately and automatically reconciles the cluster state so that the resource modification is fulfilled.

Console-based scaling of nodes and pods in NVIDIA Metropolis
OpenShift is the leading enterprise Kubernetes platform for running next-generation cloud native analytical services in hybrid and multi-cloud environments all the way to the edge, making it easy for edge platforms, like NVIDIA EGX, to acquire, stream, predict, and act upon only the required and relevant data. NVIDIA Metropolis leverages these foundational services to address use cases like traffic optimization, fleet routing, and incident predictions, contributing to creating safer, smarter, and more sustainable cities through the latest technology trends like AI, edge to cloud computing, and Internet of Things (IoT).
To experience this demo in person and to get more information about deploying these technologies in smart cities, visit the NVIDIA and Red Hat booths at the NVIDIA GTC conference in Washington, D.C. from November 4 to 6, 2019.
